

Specifications | |
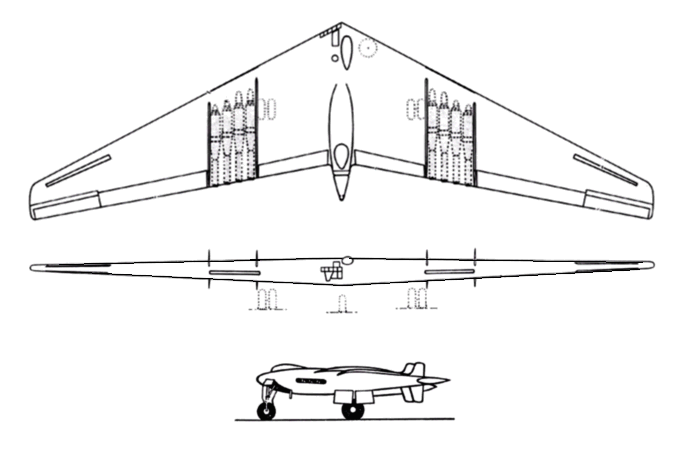
| Length | 53 ft |
| Height | 15 ft |
| Wingspan | 172 ft |
| Wing Area | 4000 Sq Ft 372 Sq M |
| Weight | 193,938 lbs / 87,953 Kg |
| Propulsion | 8 Allison J35-A-15 |
| Range | 3155 miles / 5080 Km |
| Cruise Speed | 419 mph / 674 Km/H / 364 Kt |
| Max Speed | 493 Mph 793.00 Km/H 429 Kt |
| Ceiling | 40700 Feet / 12400 M |