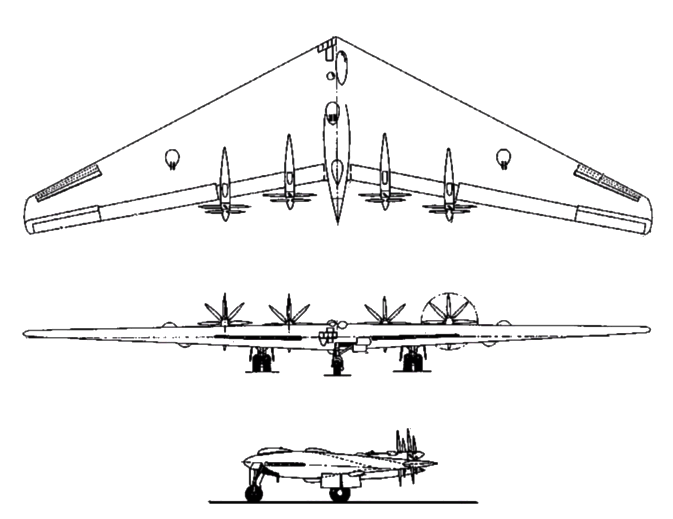








Specifications | |
| Type: | Strategic heavy bomber prototype |
| Engine: | 4 Pratt & Whitney R4360-17/25 radial piston |
| Crew: | 7 |
| Speed: | 391 mph. |
| Range: | 2,500 miles |
| Ceiling: | 40,000 ft. |
| Max Weight: | 209,000 lb. |
| Height: | 20 ft. 1 in. |
| Armament: | 20 machine guns in seven barbettes, and
up to 10,000 lb of bombs |






