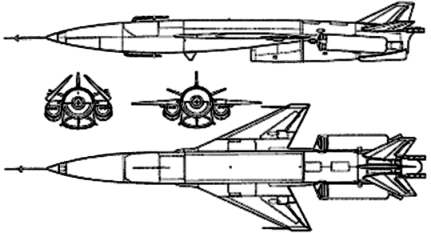
The SS-N-3 is a family of turbojet-powered, cruise missiles with three variants [confusingly, the Western nomenclature designates the initial P-5 variant with the highest number -- SS-N-3c].
The P-5 [SS-N-3c Shaddock], an inertially-guided missile, is launched from Echo II, Whiskey Conversion, and Juliett submarines and flies to a maximum range of 250 nm at a speed of . It is the oldest of the three SS-N-3 missiles and is almost identical to the Soviet Army SSC-1a (Shaddock). The P-5 cruise missile was designed in the 1950's by the Chelomey design bureau. The P-5 had a special system of two unfolding wings "ARK-5", which allowed it to be launched from the relatively low diameter cylindrical submarine launcher. P-5 had a range of 500 km at an altitude of 100-400 meters and a speed of 345 m/s [Mach 0.9]. The later P-7 variant had a range of 1000 km. These characteristics allowed the P-5 to effectively penetrate the US coastal air defense system of the early 1960's. The circular error probable at full range was 3,000m, which was compensated by the 930 Kg "RDS-4" nuclear warhead. As with the US Navy's Regulus, to fire the SS-N-3c the submarine platform had to surface for launch, deploy and activate a tracking radar, and remain on the surface linked to the high altitude cruise missile in flight via datalink, providing guidance commands based on the submarine radar's tracking data.
The P-6 [SS-N-3a Shaddock] is a more accurate cruise missile later developed for targeting US Aircraft carriers. This radar-homing missile is launched from Echo II and Juliett submarines and flies to a maximum range of 220 nm at a cruise speed of Mach 1.2. A 2200-lb conventional or nuclear warhead is estimated for the SS-N-3a. In its antiship version, the Echo depended on prior cueing by a radar-equipped maritime patrol aircraft and terminal homing by a radar seeker on the SS-N-3 itself. The high altitude, relatively slow SS-N-3 was vulnerable to air defenses in flight, and its radar seeker was vulnerable to jamming and deception measures.
The P-35 SS-N-3b (SEPAL), also a radar-homing missile, is launched from Kynda and Kresta I class guided-missile cruisers and generally flies to a range of 150 nm at a speed of Mach 1.2. It is estimated to carry a 2200-lb warhead.
The S-35 SSC-1a "SHADDOCK" missile is transported in and launched from a long cylindrical container mounted on an eight-wheel vehicle of distinctive appearance. For launching, the crew 'lowers the four hydraulic stabilization jacks, removes the hemispherical end covers to the top-mounted tables, clamps down the blast shields over the windows, and elevates the container to the proper launch angle. The SSC-lb coastal defense version can be distinguished by the longer driver's cab on the transport-launch vehicle.
Specifications | ||
| Contractor | Chelomey | |
| Entered Service | ||
| Total length |
10.20 meters [SS-N-3a/b] 11.75 meters [SS-N-3c] | |
| Diameter | 0.98 meter | |
| Wingspan | 5.00 meters | |
| Weight | 5,400 kg | |
| Warhead | ||
| Propulsion |
| |
| Maximum Speed | Mach 0.9 | |
| Maximum effective range |
450 km [SS-N-3a/b] 750 km [SS-N-3c] | |
| Guidance mode | inertial with mid-course guidance through data link from launch platform | |
| Single-shot hit probability | ||