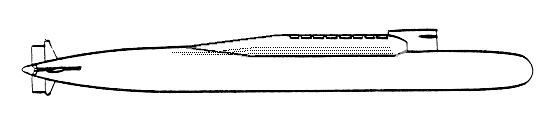



The development of the 667BDR Delta III ballistic missile submarine began in 1972 at the Rubin Central Design Bureau for Marine Engineering. This strategic submarine is equipped with the D-9R launch system and 16 R-29R missiles, and is the first submarine that can fire any number of missiles in a single salvo.
The R-29R missile is the first sea-based Soviet ballistic missile carrying 3 to 7 multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), with a range of 6,500 to 8000 km, depending on the number of reentry vehicles.
The Delta III is equipped with the "Almaz -BDR" battle management system ensuring firing of deep-water torpedos. The inertial navigational system "Tobol-BD" is of the Delta II was replaced with the "Tobol-M-1" system, and subsequently with the "Tobol-M-2". The Delta III is also equipped with the "Bumblebee" hydroacoustic navigational system to determinate its position through hydroacoustic buoys. Instead of the hydroacoustic system "Kerch" was used on the 667BD submarines, the Delta III uses the new "Rubikon" hydro-acoustic system.
The advanced Delta III SSBN entered service in 1976, and by 1982 a total of fourteen submarines were commissioned. All of them were build at Severodvinsk. The operational lifetime of these submarines is estimated to be 20-25 years. The Delta III submarines which served in the Northern fleet formed a division and were based in the port of Sayda in the Yagyelnaya bay and in the Olyenya port. In the early 90s the ballistic missile submarines were transferred to Yagyelnaya. The Delta III that served in the Pacific Fleet formed a division of SSBNs which is based on Kamchatka.
When the START-1 treaty was signed in 1991 five 667BDR SSBNs still served in the Northern (3 - in Yagyelnaya, 2 - in Olyenyey ) and nine in the Pacific Fleet. One Delta III submarine of the Northern fleet was decommissioned in 1994. The Nunn-Lugar Cooperative Threat Reduction program is scheduled to dismantle 25 Delta-class, five Typhoon-class, and one Yankee-class ballistic missile submarines capable of launching over 400 missiles with over 1,700 warheads, by the year 2003. As of September 1999 US specialists had helped disassemble one Yankee- and six Delta-class submarines, while the Russians had destroyed another five ballistic missile subs on their own using American equipment.
As of June 2000 the Russian Navy claims that it operates 26 strategic nuclear submarines carrying 2,272 nuclear warheads on 440 ballistic missiles. This force is said to consist of 5 Typhoon class submarines, 7 Delta-IV class submarines, and 13 Delta-III class submarines [which only adds up to 25, not 26 submarines]. Not all of these submarines are presently seaworthy. The Russian Navy reportedly believes that 12 strategic nuclear submarines with ballistic missiles represent the minimum necessary force structure. According to media reports a classified presidential decree of 04 March 2000 established this force goal for the period through 2010.
Specifications |
|
|
Soviet Designation |
667BDRM Dolphin |
|
US-Designation |
Delta IV |
|
Development began |
1972 |
|
Design Bureau |
Central Design Bureau for Marine Engineering "Rubin" |
|
Chief designer |
S.H. Kovalev |
|
Builders |
Nr. 402 Severodvinsk |
|
Construction and Outfit |
1975-1981 |
|
Service time |
1976- |
|
Number of ships |
7 |
|
Armament |
D-9 RM launch system with 16 R-29R missiles |
| 4-533mm torpedo tubes | |
|
Power Plant |
2 pressurized water reactors, 90 MW each |
|
Propellers |
2 � 7 blade fixed-pitch |
|
Length |
155 meters |
|
Beam |
11.7 meters |
|
Draft |
8.7 meters |
|
Displacement |
8,940 tons Surfaced 10,600 tons Submerged |
|
Operational depth |
320 meters (design) |
|
Speed |
13-14 knots Surface |
|
Crew |
130 men |
|
Endurance |
80 days |
Class Listing |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boat | Shipyard | Chronology | Notes | |||||
| # | number | Name | Laid Down | Launched | Comm. | Stricken | ||
| 1 | K-441 | 26 Zvezda KPSS | 402 Sevmash | 1975 | 1976 | 12/**/1976 | ---------- | 04/1992 unnamed 1996 in reserve |
| 2 | K-424 | 402 Sevmash | ---------- | ---------- | 1977 | ---------- | 1997 in reserve | |
| 3 | K-449 | 402 Sevmash | ---------- | ---------- | 1977 | ---------- | 1996 in reserve | |
| 4 | K-455 | 402 Sevmash | ---------- | ---------- | 1978 | ---------- | 1998-99 in reserve | |
| 5 | K-490 | 402 Sevmash | ---------- | ---------- | 1978 | ---------- | 1998-99 in reserve | |
| 6 | K-487 | 402 Sevmash | ---------- | ---------- | 1978 | ---------- | 1998-99 in reserve | |
| 7 | K-44 | 402 Sevmash | ---------- | ---------- | 1979 | ---------- | 1997 in reserve | |
| 8 | K-496 | 402 Sevmash | 1976 | 01/**/1978 | 1979 | |||
| 9 | K-506 | 402 Sevmash | 1977 | 01/**/1979 | 1979 | |||
| 10 | K-211 | 402 Sevmash | 1977 | 01/**/1979 | 1980 | |||
| 11 | K-223 | 402 Sevmash | ---------- | ---------- | 1980 | ---------- | 1998-99 in reserve | |
| 12 | K-180 | 402 Sevmash | 1978 | 12/**/1980 | 1980 | |||
| 13 | K-433 | 402 Sevmash | ---------- | ---------- | 1981 | ---------- | 1997 in reserve | |
| 14 | K-129 | 402 Sevmash | 1979 | 12/**/1981 | 1981 | ---------- | 1997 in reserve possibly still in operation | |