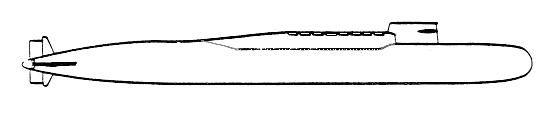



The 667BD was primarily developed to increase the number of missiles on strategic submarines. Its development was approved in June 1972 under the direction of the Rubin Central Design Bureau for Marine Engineering. The 667B Delta I served as the basis for the main design features. The pressure hull was lengthened by 16 meters in the area of the fourth and fifth compartments where four additional missile tubes were located. The displacement increased in 1,500 tons, and the full speed decreased 1 knot.
The 667BD submarines are equipped with the D-9D launch system and 16 R-29DD missiles. During the development of the new ballistic missile submarine several measures were applied to decrease the radiated noise level. The steam turbines include a two-spool system of shock-absorbers, the pipelines and hydraulic devices are isolated from the hulls and a new hydroacoustic coating was applied.
The first 667BD entered the Navy on 30 September 1975. Between 1973 and 1975 four submarines of this project were constructed at the Northern machine-building enterprise in Severodvinsk. The 667BD submarines formed part of the 3rd flotilla of submarines of the Northern fleet based in the Yagyelnaya bay. In 1996 one submarine was removed from operational status.
It is anticipated that all 667BD submarines will be decommissioned in compliance with the provisions of the START-1 treaty.
The Nunn-Lugar Cooperative Threat Reduction program is scheduled to dismantle 25 Delta-class, five Typhoon-class, and one Yankee-class ballistic missile submarines capable of launching over 400 missiles with over 1,700 warheads, by the year 2003. As of September 1999 US specialists had helped disassemble one Yankee- and six Delta-class submarines, while the Russians had destroyed another five ballistic missile subs on their own using American equipment.
Specifications |
|||
|
Soviet Designation |
667B Murena |
667 BD Murena-M |
|
|
US-Designation |
Delta I |
Delta II |
|
|
Development began |
1965 |
November 1967 |
|
|
Design Bureau |
Central Design Bureau for Marine Engineering "Rubin" |
||
|
Chief designer |
S.H. Kovalev |
||
|
Builders |
Severodvinsk Komsomol Na Amur |
Severodvinsk | |
|
Construction and Outfit |
1971-1977 |
1973-1975 |
|
|
Service time |
1973- |
1975-1996 |
|
|
Number of ships |
18 |
4 |
|
|
Armament |
D-9 launch system with |
D-9 launch system with |
|
| 4-533mm torpedo tubes |
4-533mm torpedo tubes 2-400mm torpedo tubes |
||
|
Power Plant |
2 pressurized water reactors |
||
|
2 steam turbines, 52.000 hp each |
2 steam turbines, 55.000 hp each |
||
|
Length |
139 meters |
155 meters |
|
|
Beam |
12 meters |
||
|
Deposit |
9 meters |
||
|
Displacement |
9000 m3 Surfaced |
10500 m3 Submerged |
|
|
11000m3 Surfaced |
13000 m3 Submerged |
||
|
Operating depth |
390 meters (design) |
||
|
Speed |
12 knots Surface |
||
|
25 knots Submerged |
24 knots Submerged |
||
|
Crew |
120 men |
130 men |
|
|
Endurance |
80 days |
||
Class Listing |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boat | Shipyard | Chronology | Notes | |||||
| # | number | Name | Laid Down | Launched | Comm. | Stricken | ||
| 1 | K-182 | Shestidesyatiletie Velikogo Oktyabrya | 402 Sevmash | 04/**/1973 | 01/**/1975 | 09/20/1975 | ---------- | 11/04/1977 named 1996 in reserve |
| 2 | K-92 | 402 Sevmash | 04/**/1973 | 01/**/1975 | 12/17/1975 | ---------- | 1996 in reserve | |
| 3 | K-193 | 402 Sevmash | 1974 | 1975 | 12/30/1975 | 1999 | 12/1997 prepared for decommissioning 1999 dismantled | |
| 4 | K-421 | 402 Sevmash | 1974 | 1975 | 12/30/1975 | ---------- | 1996 in reserve 2000 planned to be defuelled | |