


Science Research, Xi'an Xi'an, Shannxi P.O.Box 69 Post Code 710024 Tel (029)3263268 Fax (029)3263333
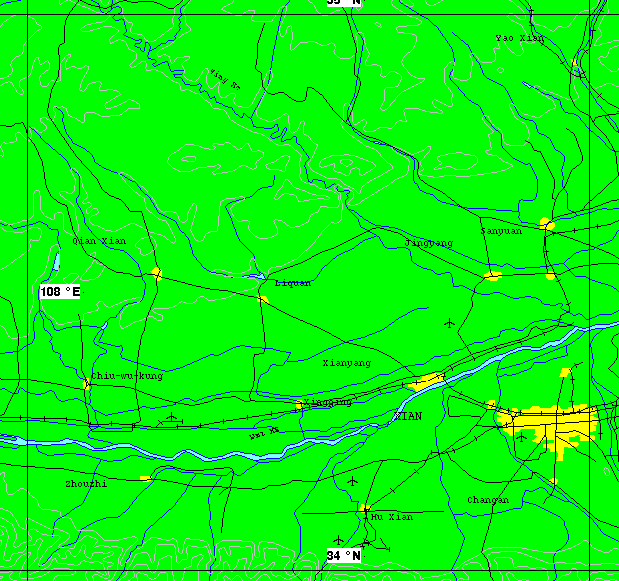
The Northwest Institute of Nuclear Technology (NINT), also known as the Northwest Nuclear Technology Research Institute, is a comprehensive multi-disciplinary research institution with more than 700 research personnel that provided diagnostic support for the nuclear weapons test program. This facility is probably located about 5 nautical miles southwest of Xi'an proper.
The Northwest Institute of Nuclear Technology (NINT) is developing a key role in CTBT verification. The Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA), has completed a contract with the Northwest Institute of Nuclear Technology (NINT) for the provision of two specially equipped vehicles developed to facilitate the detection and monitoring of radionuclide contamination of the environment.
The US Bureau of Export Administration (BXA) issued a final rule, effective May 28, 1999, which amends the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) by adding the Northwest Institute of Nuclear Technology to the Entity List (15 CFR Part 744, Supplement No. 4), along with five other Chinese entities. As a result of these additions to the Entity List a license will be required for the export or reexport of all items subject to the EAR to Northwest Institute of Nuclear Technology. All license applications for exports or reexports will be reviewed on a case-by-case basis to determine whether the export or reexport would materially contribute to the proliferation of missiles. The new restrictions are the result of intelligence gathered by the US.
Research conducted at NINT has included analysis of numerical computational results of system generated electromagnetic pulse [SGEMP] effects. SGEMP is a type of EMP that is generated by the pulse X-ray radiation on the surface of satellites and missiles. This analysis can be the theoretical base for experimental measurements.
Taking the nuclear applied technology as the dominant sector, disciplines include pulsed beam measurement, radiation effect simulation and anti-radiation reinforcement, quasi-molecule laser, high-power microwave, pulse power, radiochemistry and radioanalytical chemistry, inorganic fluoride synthesis and applications, materials modification by irradiation, computer simulation, and visualization technique, explosive mechanics and explosive physics, microcomputer control, and industrial automation. Main facilities include large-sized simulation experimental facilities: 0.9 MV, 0.9 MA and 1 MV, 30 kA relativistic electron-beam accelerator, ELV8 electron irradiation accelerator, RS-20 repeated frequency electron accelerator, 200KJ high-density plasma focusing device, T-400 and K-400 neutron generator, 300,000 Ci cobalt source, 57 mm and 130 mm gas guns, inorganic fluorides production equipment, operating station for small-sized giant��scale computer and medium-scale computer and computer network system. As of the late 1990s the Institute was constructing a pulse reactor and a laboratory to initiate radiation effect simulation. The Institute has effected a large number of national research projects and research achievements, nearly 50 gained national awards and over 1 000 ministry or commission prizes. Paying a great attention to study and develop the applied engineering technology, and by using the necessary laboratories and advanced equipment and instruments, the Institute, in recent years, has successively completed many projects, e.g. computerized remote-control system of urban class-2 water supply, wireless communication network for tax bureau, optical fibre engineering of traffic control system, automatic control of the temperature and humidity for spinning workshop of cotton mills, and also developed many new products, including ATS automatic target checking system, LD-3 lighting monitoring system, nuclear material levelmeter, SX-A intelligent pulse imaging system, arbitrary waveform signal generator, optic fibre and cable pecker, and thermal shrinking materials. The Institute has kept close co-operations with more than 20 institutes in nearly 10 countries and regions worldwide.